
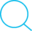

struct _IO_FILE {
int _flags; /* High-order word is _IO_MAGIC; rest is flags. */
#define _IO_file_flags _flags
/* The following pointers correspond to the C++ streambuf protocol. */
/* Note: Tk uses the _IO_read_ptr and _IO_read_end fields directly. */
char* _IO_read_ptr; /* Current read pointer */
char* _IO_read_end; /* End of get area. */
char* _IO_read_base; /* Start of putback+get area. */
char* _IO_write_base; /* Start of put area. */
char* _IO_write_ptr; /* Current put pointer. */
char* _IO_write_end; /* End of put area. */
char* _IO_buf_base; /* Start of reserve area. */
char* _IO_buf_end; /* End of reserve area. */
/* The following fields are used to support backing up and undo. */
char *_IO_save_base; /* Pointer to start of non-current get area. */
char *_IO_backup_base; /* Pointer to first valid character of backup area */
char *_IO_save_end; /* Pointer to end of non-current get area. */
struct _IO_marker *_markers;
struct _IO_FILE *_chain;
int _fileno;
#if 0
int _blksize;
#else
int _flags2;
#endif
_IO_off_t _old_offset; /* This used to be _offset but it's too small. */
#define __HAVE_COLUMN /* temporary */
/* 1+column number of pbase(); 0 is unknown. */
unsigned short _cur_column;
signed char _vtable_offset;
char _shortbuf[1];
/* char* _save_gptr; char* _save_egptr; */
_IO_lock_t *_lock;
#ifdef _IO_USE_OLD_IO_FILE
};
flags标志该FILE的行为,高两位字节由libc决定,低两位字节规则如下
#define _IO_MAGIC 0xFBAD0000 /* Magic number */
#define _OLD_STDIO_MAGIC 0xFABC0000 /* Emulate old stdio. */
#define _IO_MAGIC_MASK 0xFFFF0000
#define _IO_USER_BUF 1 /* User owns buffer; don't delete it on close. */
#define _IO_UNBUFFERED 2
#define _IO_NO_READS 4 /* Reading not allowed */
#define _IO_NO_WRITES 8 /* Writing not allowd */
#define _IO_EOF_SEEN 0x10
#define _IO_ERR_SEEN 0x20
#define _IO_DELETE_DONT_CLOSE 0x40 /* Don't call close(_fileno) on cleanup. */
#define _IO_LINKED 0x80 /* Set if linked (using _chain) to streambuf::_list_all.*/
#define _IO_IN_BACKUP 0x100
#define _IO_LINE_BUF 0x200
#define _IO_TIED_PUT_GET 0x400 /* Set if put and get pointer logicly tied. */
#define _IO_CURRENTLY_PUTTING 0x800
#define _IO_IS_APPENDING 0x1000
#define _IO_IS_FILEBUF 0x2000
#define _IO_BAD_SEEN 0x4000
#define _IO_USER_LOCK 0x8000
储存文件描述符
pwndbg> print stdout
$1 = (struct _IO_FILE *) 0x7fffff3ec760 <_IO_2_1_stdout_>`
pwndbg> ptype stdout
type = struct _IO_FILE {
int _flags;
char *_IO_read_ptr;
char *_IO_read_end;
char *_IO_read_base;
char *_IO_write_base;
char *_IO_write_ptr;
char *_IO_write_end;
char *_IO_buf_base;
char *_IO_buf_end;
char *_IO_save_base;
char *_IO_backup_base;
char *_IO_save_end;
struct _IO_marker *_markers;
struct _IO_FILE *_chain;
int _fileno;
int _flags2;
__off_t _old_offset;
unsigned short _cur_column;
signed char _vtable_offset;
char _shortbuf[1];
_IO_lock_t *_lock;
__off64_t _offset;
struct _IO_codecvt *_codecvt;
struct _IO_wide_data *_wide_data;
struct _IO_FILE *_freeres_list;
void *_freeres_buf;
size_t __pad5;
int _mode;
char _unused2[20];
} *
pwndbg> x/64gx 0x7fffff3ec760
0x7fffff3ec760 <_IO_2_1_stdout_>: 0x00000000fbad2887 0x00007fffff3ec7e3
0x7fffff3ec770 <_IO_2_1_stdout_+16>: 0x00007fffff3ec7e3 0x00007fffff3ec7e3
0x7fffff3ec780 <_IO_2_1_stdout_+32>: 0x00007fffff3ec7e3 0x00007fffff3ec7e3
0x7fffff3ec790 <_IO_2_1_stdout_+48>: 0x00007fffff3ec7e3 0x00007fffff3ec7e3
0x7fffff3ec7a0 <_IO_2_1_stdout_+64>: 0x00007fffff3ec7e4 0x0000000000000000
0x7fffff3ec7b0 <_IO_2_1_stdout_+80>: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x7fffff3ec7c0 <_IO_2_1_stdout_+96>: 0x0000000000000000 0x00007fffff3eba00
0x7fffff3ec7d0 <_IO_2_1_stdout_+112>: 0x0000000000000001 0xffffffffffffffff
0x7fffff3ec7e0 <_IO_2_1_stdout_+128>: 0x000000000a000000 0x00007fffff3ed8c0
0x7fffff3ec7f0 <_IO_2_1_stdout_+144>: 0xffffffffffffffff 0x0000000000000000
0x7fffff3ec800 <_IO_2_1_stdout_+160>: 0x00007fffff3eb8c0 0x0000000000000000
0x7fffff3ec810 <_IO_2_1_stdout_+176>: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x7fffff3ec820 <_IO_2_1_stdout_+192>: 0x00000000ffffffff 0x0000000000000000
0x7fffff3ec830 <_IO_2_1_stdout_+208>: 0x0000000000000000 0x00007fffff3e82a0
_IO_MAGIC|_IO_IS_FILEBUF|_IO_CURRENTLY_PUTTING|_IO_LINKED|_IO_NO_READS | _IO_UNBUFFERED |_IO_USER_BUF = 0xfbad2887
ioputs
#include "libioP.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <limits.h>
int
_IO_puts (const char *str)
{
int result = EOF;
_IO_size_t len = strlen (str);
_IO_acquire_lock (_IO_stdout);
if ((_IO_vtable_offset (_IO_stdout) != 0
|| _IO_fwide (_IO_stdout, -1) == -1)
&& _IO_sputn (_IO_stdout, str, len) == len
&& _IO_putc_unlocked ('\n', _IO_stdout) != EOF)
result = MIN (INT_MAX, len + 1);
_IO_release_lock (_IO_stdout);
return result;
}
weak_alias (_IO_puts, puts)
调用_IO_sputn
#define _IO_sputn(__fp, __s, __n) _IO_XSPUTN (__fp, __s, __n)
__xsputn = 0x7ffff7a6f930 <_IO_new_file_xsputn>
_IO_sputn 调用vtable 中的 ` _IO_XSPUTN,即_IO_new_file_xsputn `
_IO_size_t
_IO_new_file_xsputn (_IO_FILE *f, const void *data, _IO_size_t n)
{
const char *s = (const char *) data;
_IO_size_t to_do = n;
int must_flush = 0;
_IO_size_t count = 0;
if (n <= 0)
return 0;
/* This is an optimized implementation.
If the amount to be written straddles a block boundary
(or the filebuf is unbuffered), use sys_write directly. */
/* First figure out how much space is available in the buffer. */
if ((f->_flags & _IO_LINE_BUF) && (f->_flags & _IO_CURRENTLY_PUTTING))
{
count = f->_IO_buf_end - f->_IO_write_ptr;
if (count >= n)
{
const char *p;
for (p = s + n; p > s; )
{
if (*--p == '\n')
{
count = p - s + 1;
must_flush = 1;
break;
}
}
}
}
else if (f->_IO_write_end > f->_IO_write_ptr)
count = f->_IO_write_end - f->_IO_write_ptr; /* Space available. */
/* Then fill the buffer. */
if (count > 0)
{
if (count > to_do)
count = to_do;
f->_IO_write_ptr = __mempcpy (f->_IO_write_ptr, s, count);
s += count;
to_do -= count;
}
if (to_do + must_flush > 0)
{
_IO_size_t block_size, do_write;
/* Next flush the (full) buffer. */
if (_IO_OVERFLOW (f, EOF) == EOF)
/* If nothing else has to be written we must not signal the
caller that everything has been written. */
return to_do == 0 ? EOF : n - to_do;
/* Try to maintain alignment: write a whole number of blocks. */
block_size = f->_IO_buf_end - f->_IO_buf_base;
do_write = to_do - (block_size >= 128 ? to_do % block_size : 0);
if (do_write)
{
count = new_do_write (f, s, do_write);
to_do -= count;
if (count < do_write)
return n - to_do;
}
/* Now write out the remainder. Normally, this will fit in the
buffer, but it's somewhat messier for line-buffered files,
so we let _IO_default_xsputn handle the general case. */
if (to_do)
to_do -= _IO_default_xsputn (f, s+do_write, to_do);
}
return n - to_do;
}
libc_hidden_ver (_IO_new_file_xsputn, _IO_file_xsputn)
判断缓冲区是否够用,然后文件指针写入,在执行输出之前调用_IO_OVERFLOW ,进行一个判断
#define _IO_OVERFLOW(FP, CH) JUMP1 (__overflow, FP, CH)
__overflow = 0x7ffff7a71300 <_IO_new_file_overflow>
int
_IO_new_file_overflow (_IO_FILE *f, int ch)
{
if (f->_flags & _IO_NO_WRITES) /* SET ERROR */
{
f->_flags |= _IO_ERR_SEEN;
__set_errno (EBADF);
return EOF;
}
/* If currently reading or no buffer allocated. */
if ((f->_flags & _IO_CURRENTLY_PUTTING) == 0 || f->_IO_write_base == NULL)
{
/* Allocate a buffer if needed. */
if (f->_IO_write_base == NULL)
{
_IO_doallocbuf (f);
_IO_setg (f, f->_IO_buf_base, f->_IO_buf_base, f->_IO_buf_base);
}
/* Otherwise must be currently reading.
If _IO_read_ptr (and hence also _IO_read_end) is at the buffer end,
logically slide the buffer forwards one block (by setting the
read pointers to all point at the beginning of the block). This
makes room for subsequent output.
Otherwise, set the read pointers to _IO_read_end (leaving that
alone, so it can continue to correspond to the external position). */
if (__glibc_unlikely (_IO_in_backup (f)))
{
size_t nbackup = f->_IO_read_end - f->_IO_read_ptr;
_IO_free_backup_area (f);
f->_IO_read_base -= MIN (nbackup,
f->_IO_read_base - f->_IO_buf_base);
f->_IO_read_ptr = f->_IO_read_base;
}
if (f->_IO_read_ptr == f->_IO_buf_end)
f->_IO_read_end = f->_IO_read_ptr = f->_IO_buf_base;
f->_IO_write_ptr = f->_IO_read_ptr;
f->_IO_write_base = f->_IO_write_ptr;
f->_IO_write_end = f->_IO_buf_end;
f->_IO_read_base = f->_IO_read_ptr = f->_IO_read_end;
f->_flags |= _IO_CURRENTLY_PUTTING;
if (f->_mode <= 0 && f->_flags & (_IO_LINE_BUF | _IO_UNBUFFERED))
f->_IO_write_end = f->_IO_write_ptr;
}
if (ch == EOF)
return _IO_do_write (f, f->_IO_write_base,
f->_IO_write_ptr - f->_IO_write_base);
if (f->_IO_write_ptr == f->_IO_buf_end ) /* Buffer is really full */
if (_IO_do_flush (f) == EOF)
return EOF;
*f->_IO_write_ptr++ = ch;
if ((f->_flags & _IO_UNBUFFERED)
|| ((f->_flags & _IO_LINE_BUF) && ch == '\n'))
if (_IO_do_write (f, f->_IO_write_base,
f->_IO_write_ptr - f->_IO_write_base) == EOF)
return EOF;
return (unsigned char) ch;
}
libc_hidden_ver (_IO_new_file_overflow, _IO_file_overflow)
第一个判断
if (f->_flags & _IO_NO_WRITES) /* SET ERROR */
{
f->_flags |= _IO_ERR_SEEN;
__set_errno (EBADF);
return EOF;
}
stdout的_IO_NO_WRITES标志位不为1,可以直接过去
第二个判断
if ((f->_flags & _IO_CURRENTLY_PUTTING) == 0 || f->_IO_write_base == NULL)
把_IO_CURRENTLY_PUTTING置为1绕过
然后到这个判断
if (ch == EOF)
return _IO_do_write (f, f->_IO_write_base,
f->_IO_write_ptr - f->_IO_write_base);
_IO_do_write
int
_IO_new_do_write (_IO_FILE *fp, const char *data, _IO_size_t to_do)
{
return (to_do == 0
|| (_IO_size_t) new_do_write (fp, data, to_do) == to_do) ? 0 : EOF;
}
libc_hidden_ver (_IO_new_do_write, _IO_do_write)
new_do_write
static
_IO_size_t
new_do_write (_IO_FILE *fp, const char *data, _IO_size_t to_do)
{
_IO_size_t count;
if (fp->_flags & _IO_IS_APPENDING)
/* On a system without a proper O_APPEND implementation,
you would need to sys_seek(0, SEEK_END) here, but is
not needed nor desirable for Unix- or Posix-like systems.
Instead, just indicate that offset (before and after) is
unpredictable. */
fp->_offset = _IO_pos_BAD;
else if (fp->_IO_read_end != fp->_IO_write_base)
{
_IO_off64_t new_pos
= _IO_SYSSEEK (fp, fp->_IO_write_base - fp->_IO_read_end, 1);
if (new_pos == _IO_pos_BAD)
return 0;
fp->_offset = new_pos;
}
count = _IO_SYSWRITE (fp, data, to_do);
if (fp->_cur_column && count)
fp->_cur_column = _IO_adjust_column (fp->_cur_column - 1, data, count) + 1;
_IO_setg (fp, fp->_IO_buf_base, fp->_IO_buf_base, fp->_IO_buf_base);
fp->_IO_write_base = fp->_IO_write_ptr = fp->_IO_buf_base;
fp->_IO_write_end = (fp->_mode <= 0
&& (fp->_flags & (_IO_LINE_BUF | _IO_UNBUFFERED))
? fp->_IO_buf_base : fp->_IO_buf_end);
return count;
}
目标是 count = _IO_SYSWRITE (fp, data, to_do);
#define _IO_SYSWRITE(FP, DATA, LEN) JUMP2 (__write, FP, DATA, LEN)
正常执行这个函数需要把_IO_IS_APPENDIN 标志位置为1
或者使stdout->_IO_read_end == stdout->_IO_write_base
综上,满足条件的flags为
#define _IO_MAGIC 0xFBAD0000 /* Magic number */
#define _IO_NO_WRITES 8 /* Writing not allowd */
#define _IO_CURRENTLY_PUTTING 0x800
#define _IO_IS_APPENDING 0x1000
_flags = 0xfbad0000 // Magic number
_flags & = ~_IO_NO_WRITES // _flags = 0xfbad0000
_flags | = _IO_CURRENTLY_PUTTING // _flags = 0xfbad0800
_flags | = _IO_IS_APPENDING // _flags = 0xfbad1800
在执行puts时会打印出内存中的一段数据,这段数据中会存在libc中的某个地址
本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际许可协议(CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)进行许可。
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).