
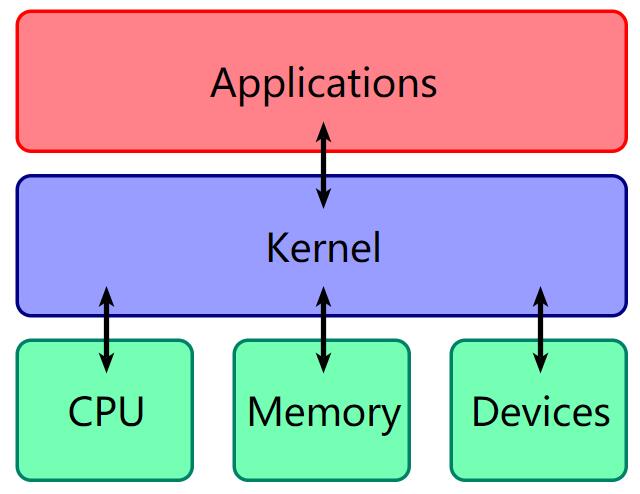
intel CPU 将 CPU 的特权级别分为 4 个级别:Ring 0, Ring 1, Ring 2, Ring 3,内层 Ring 可以随便使用外层 Ring 的资源
老千层饼了
大多数操作系统(Linux,OSX,Windows)都只使用了Ring3和Ring0
LKM,可加载核心模块,内核模块
运行在内核空间的应用程序,包括驱动程序和内核扩展模块
LKM文件格式和用户态的可执行程序相同,但不能单独运行,只能链接到内核作为内核的一部分运行
insmod:加载模块
rmmod:卸载模块
lsmod:列出已加载模块
LKM是最常见的查找漏洞的地方
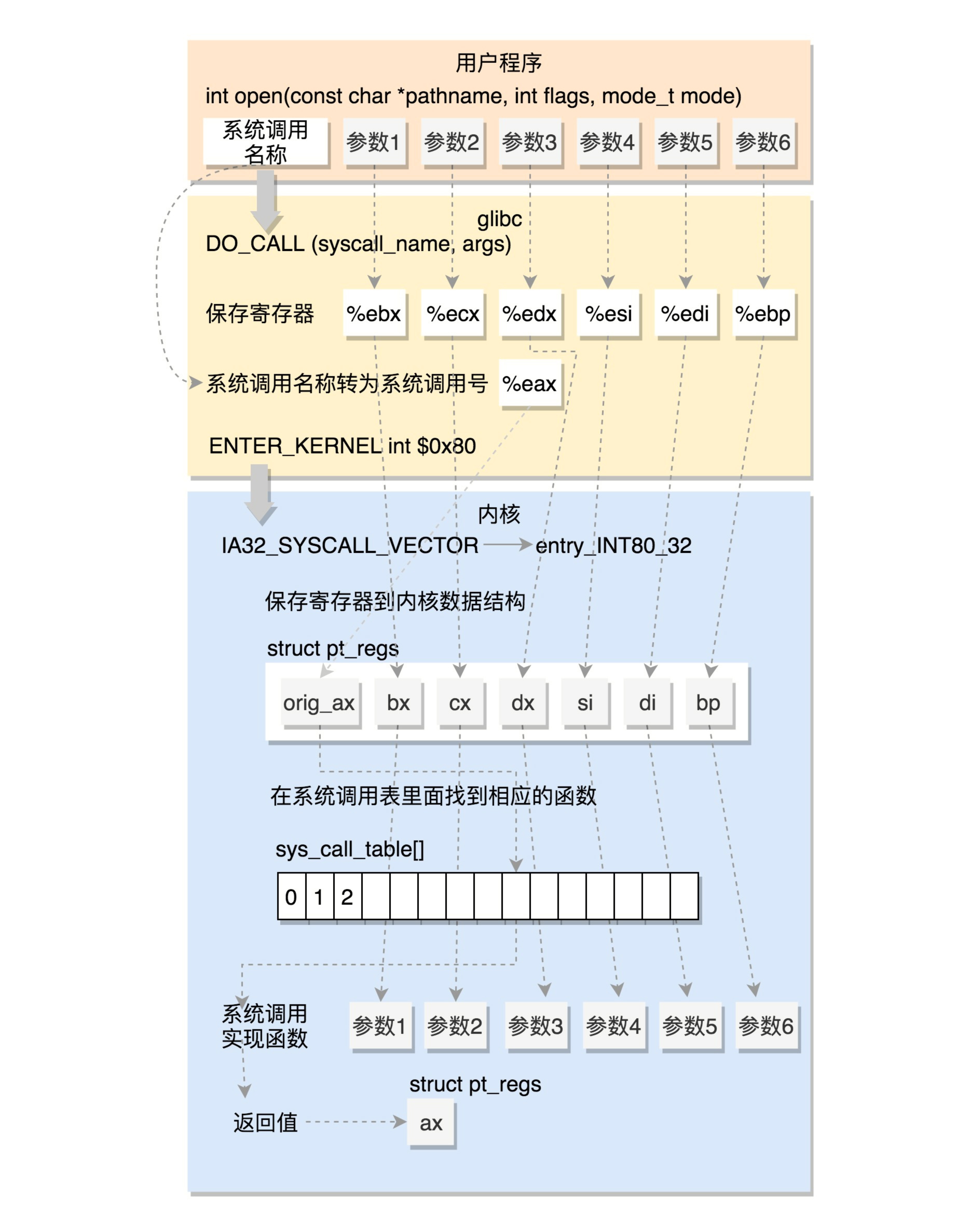
发生用户态内核态状态切换的三种情况
系统调用,提供用户态程序与内核的接口,通过系统调用用户态程序可以请求更高权限的服务
x86
x64
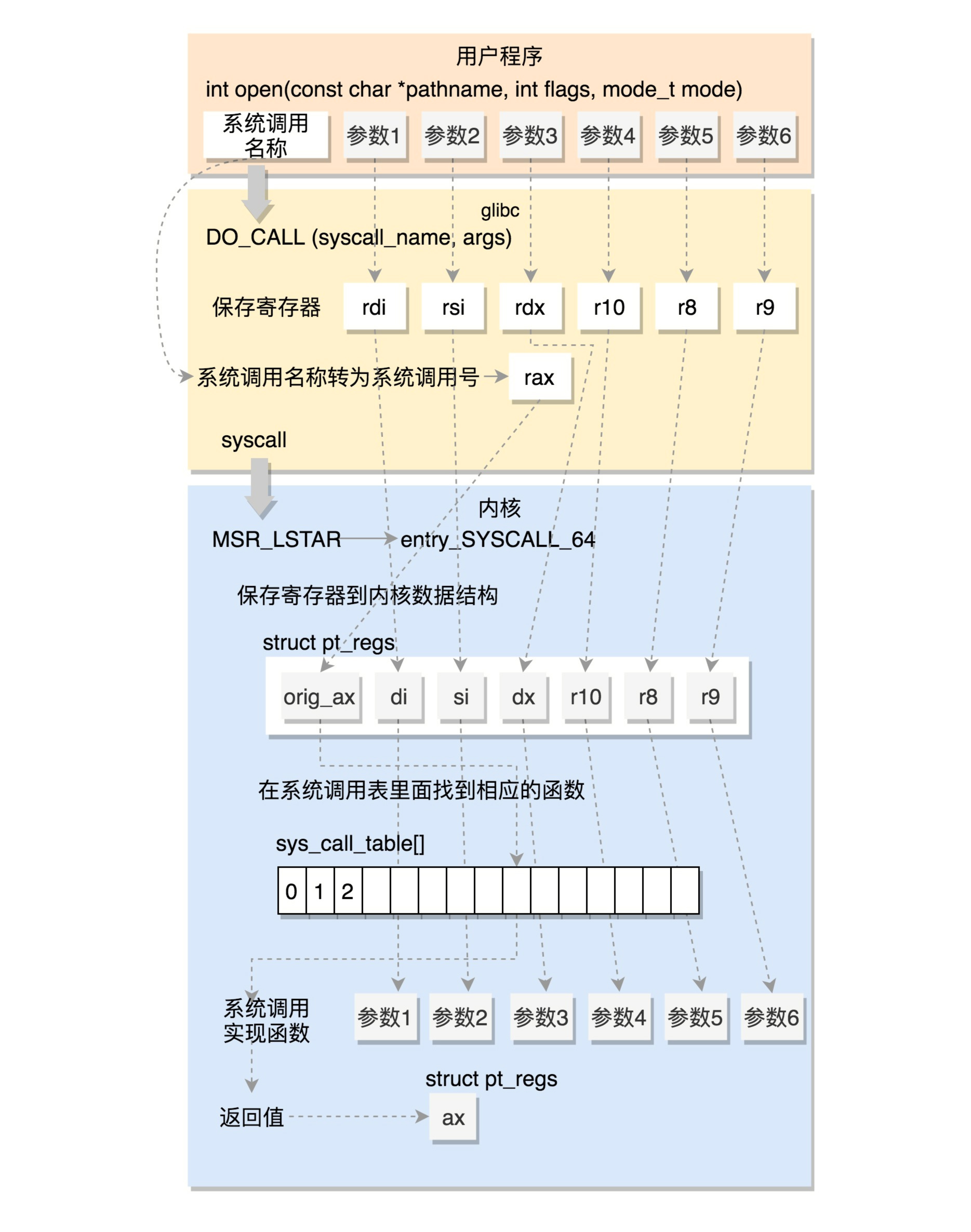
用户态切换到内核态
通过swapgs指令交换 GS 段选择符及 MSR_KERNEL_GS_BASE 特殊模式寄存器中的值
保存用户空间栈顶,当前处理器的栈顶放入rsp
movq %rsp, PER_CPU_VAR(rsp_scratch)
movq PER_CPU_VAR(cpu_current_top_of_stack), %rsp
pushq $__USER_DS
pushq PER_CPU_VAR(rsp_scratch)
保存各寄存器值
ENABLE_INTERRUPTS(CLBR_NONE)
pushq %r11
pushq $__USER_CS
pushq %rcx
pushq %rax
pushq %rdi
pushq %rsi
pushq %rdx
pushq %rcx
pushq $-ENOSYS
pushq %r8
pushq %r9
pushq %r10
pushq %r11
sub $(6*8), %rsp
rax - 系统调用号
rcx - 用户空间返回地址
r11 - rflags
rdi - 第1个参数
rsi - 第2个参数
rdx - 第3个参数
r10 - 第4个参数
r8 - 第5个参数
r9 - 第6个参数
判断是否禁用x32_abi,如果禁用,使用rax的值和系统调用数比较,否则用eax
#if __SYSCALL_MASK == ~0
cmpq $__NR_syscall_max, %rax
#else
andl $__SYSCALL_MASK, %eax
cmpl $__NR_syscall_max, %eax
#endif
根据系统调用号跳系统调用表
movq %r10, %rcx
call *sys_call_table(, %rax, 8)
内核态切换到用户态
恢复除rcx和r11外所有通用寄存器,将返回地址放入rcx,将标志放入r11,原来的栈顶放入rsp
RESTORE_C_REGS_EXCEPT_RCX_R11
movq RIP(%rsp), %rcx
movq EFLAGS(%rsp), %r11
movq RSP(%rsp), %rsp
USERGS_SYSRET64
调用宏USERGS_SYSRET64,使用swapgs指令交换GS,然后sysretq
#define USERGS_SYSRET64 \
swapgs; \
sysretq;
用户态程序发生异常时,切换到内核态执行相关异常处理
外部设备完成请求后向CPU发出中断信号,CPU暂停执行下一条指令,处理中断信号
如果之前执行的指令是用户态,就会切换到内核态
int ioctl(int fd, unsigned long request, ...)
fd是打开设备返回的文件描述符,后面是用户程序对设备的控制命令
NAME
ioctl - control device
SYNOPSIS
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
int ioctl(int fd, unsigned long request, ...);
DESCRIPTION
The ioctl() system call manipulates the underlying device parameters of special
files. In particular, many operating characteristics of character special
files (e.g., terminals) may be controlled with ioctl() requests. The argument
fd must be an open file descriptor.
The second argument is a device-dependent request code. The third argument is
an untyped pointer to memory. It's traditionally char *argp (from the days
before void * was valid C), and will be so named for this discussion.
An ioctl() request has encoded in it whether the argument is an in parameter or
out parameter, and the size of the argument argp in bytes. Macros and defines
used in specifying an ioctl() request are located in the file <sys/ioctl.h>.
用于与设备通信
在/proc/kallsyms可以查看函数地址
/ $ grep commit_creds /proc/kallsyms
ffffffff810a1420 T commit_creds
ffffffff81d88f60 R __ksymtab_commit_creds
ffffffff81da84d0 r __kcrctab_commit_creds
ffffffff81db948c r __kstrtab_commit_creds
限制查看
echo 1 > /proc/sys/kernel/kptr_restrict
printfk()
内容⑧一定在终端,一定在内核缓冲区
dmesg可以查看
限制非特权用户读取dmesg信息
echo 1 > /proc/sys/kernel/dmesg_restrict
copy_from_user(),copy_to_user()
将用户空间的数据传送到内核空间
将内核空间的数据传送到用户空间
kmalloc(),kfree()
内核态的内存分配函数
使用slab/slub分配器
int commit_creds(struct cred *new)
更新进程creds
struct cred* prepare_kernel_cred(struct task_struct* daemon)
创建cred struct
提权commit_creds(prepare_kernel_cred(0))
虚拟文件系统
对虚拟文件的读写可以实现与内核的通信
创建虚拟文件
struct proc_dir_entry *create_proc_entry( const char *name, mode_t mode, struct proc_dir_entry *parent );
static inline struct proc_dir_entry *proc_create(const char *name, umode_t mode, struct proc_dir_entry *parent,const struct file_operations *proc_fops)
//truct proc_dir_entry *parent默认为/proc
删除虚拟文件
void remove_proc_entry( const char *name, struct proc_dir_entry *parent );
////truct proc_dir_entry *parent默认为/proc
cred结构体记录进程权限
struct cred {
atomic_t usage;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_CREDENTIALS
atomic_t subscribers; /* number of processes subscribed */
void *put_addr;
unsigned magic;
#define CRED_MAGIC 0x43736564
#define CRED_MAGIC_DEAD 0x44656144
#endif
kuid_t uid; /* real UID of the task */
kgid_t gid; /* real GID of the task */
kuid_t suid; /* saved UID of the task */
kgid_t sgid; /* saved GID of the task */
kuid_t euid; /* effective UID of the task */
kgid_t egid; /* effective GID of the task */
kuid_t fsuid; /* UID for VFS ops */
kgid_t fsgid; /* GID for VFS ops */
unsigned securebits; /* SUID-less security management */
kernel_cap_t cap_inheritable; /* caps our children can inherit */
kernel_cap_t cap_permitted; /* caps we're permitted */
kernel_cap_t cap_effective; /* caps we can actually use */
kernel_cap_t cap_bset; /* capability bounding set */
kernel_cap_t cap_ambient; /* Ambient capability set */
#ifdef CONFIG_KEYS
unsigned char jit_keyring; /* default keyring to attach requested
* keys to */
struct key __rcu *session_keyring; /* keyring inherited over fork */
struct key *process_keyring; /* keyring private to this process */
struct key *thread_keyring; /* keyring private to this thread */
struct key *request_key_auth; /* assumed request_key authority */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
void *security; /* subjective LSM security */
#endif
struct user_struct *user; /* real user ID subscription */
struct user_namespace *user_ns; /* user_ns the caps and keyrings are relative to. */
struct group_info *group_info; /* supplementary groups for euid/fsgid */
struct rcu_head rcu; /* RCU deletion hook */
} __randomize_layout;
除了用户态程序的保护机制还有:
SMAP/SMEP
SMAP
Supervisor Mode Access Prevention,管理模式访问保护
禁止内核访问用户空间的数据
SMEP
Supervisor Mode Execution Prevention,管理模式执行保护
禁止内核执行用户空间的代码
arm中称为PXN(Privileged Execute Never)
-cpu qemu64,smep,smap 2>/dev/null
mmap_min_addr
内核空间和用户空间共享虚拟内存地址,需要防止用户空间mmap的内存从0开始,缓解NULL解引用攻击
mmap_min_addr设置被内置到内核中(x86为64k,arm为32k)
boot.sh
kernel启动脚本,一般用qemu,根据参数可以查看保护情况
rootfs.cpio
文件系统映像
vmlinux
静态编译,未压缩的内核文件
可以找gadget
ROPgadget不好使,太慢
ropper --file ./vmlinux --nocolor
bzImage
压缩后的内核文件
可以提取出vmlinux,脚本https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/master/scripts/extract-vmlinux
#!/bin/sh
# SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0-only
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
# extract-vmlinux - Extract uncompressed vmlinux from a kernel image
#
# Inspired from extract-ikconfig
# (c) 2009,2010 Dick Streefland <dick@streefland.net>
#
# (c) 2011 Corentin Chary <corentin.chary@gmail.com>
#
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
check_vmlinux()
{
# Use readelf to check if it's a valid ELF
# TODO: find a better to way to check that it's really vmlinux
# and not just an elf
readelf -h $1 > /dev/null 2>&1 || return 1
cat $1
exit 0
}
try_decompress()
{
# The obscure use of the "tr" filter is to work around older versions of
# "grep" that report the byte offset of the line instead of the pattern.
# Try to find the header ($1) and decompress from here
for pos in `tr "$1\n$2" "\n$2=" < "$img" | grep -abo "^$2"`
do
pos=${pos%%:*}
tail -c+$pos "$img" | $3 > $tmp 2> /dev/null
check_vmlinux $tmp
done
}
# Check invocation:
me=${0##*/}
img=$1
if [ $# -ne 1 -o ! -s "$img" ]
then
echo "Usage: $me <kernel-image>" >&2
exit 2
fi
# Prepare temp files:
tmp=$(mktemp /tmp/vmlinux-XXX)
trap "rm -f $tmp" 0
# That didn't work, so retry after decompression.
try_decompress '\037\213\010' xy gunzip
try_decompress '\3757zXZ\000' abcde unxz
try_decompress 'BZh' xy bunzip2
try_decompress '\135\0\0\0' xxx unlzma
try_decompress '\211\114\132' xy 'lzop -d'
try_decompress '\002!L\030' xxx 'lz4 -d'
try_decompress '(\265/\375' xxx unzstd
# Finally check for uncompressed images or objects:
check_vmlinux $img
# Bail out:
echo "$me: Cannot find vmlinux." >&2
init文件
解压rootfs.cpio得到,记录系统初始化时的操作
ko文件
解压rootfs.cpio得到,有漏洞的程序
解压rootfs.cpio
cpio -idmv < rootfs.cpio
打包rootfs.cpio
find . | cpio -o --format=newc > rootfs.cpio
qemu
-initrd rootfs.cpio,使用 rootfs.cpio 作为内核启动的文件系统
-kernel bzImage,使用 bzImage 作为 kernel 映像
-cpu kvm64,+smep,设置 CPU 的安全选项
-m 64M,设置虚拟 RAM 为 64M,默认为 128M
gdb调试
修改init文件可以直接root,方便调试
setsid /bin/cttyhack setuidgid 0 /bin/sh
boot.sh中qemu参数加上-s ,开gdbserver监听端口1234
gdb连接
target remote : 1234
找ko文件text段地址
cat /sys/module/文件名/sections/.text
gdb中添加符号表
add-symbol-file
查看slab信息
cat /proc/slabinfo
LKM
insmod:加载模块
rmmod:卸载模块
lsmod:列出已加载模块
查看模块加载基址
cat /sys/module/模块名称/sections/.text
查看内核基址
cat /proc/kallsyms | grep startup_64
ffffffff81000000 T startup_64
查看函数地址
grep 函数名称 /proc/kallsyms
查看内核缓冲区
dmesg
本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际许可协议(CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)进行许可。
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).